Research
Learn more about requesting scientific collaboration with IPDC.
Key offerings for diverse modality imaging:
| 
|
Fluorescent/Optical Imaging (Fluorescent/optical and multiple dyes)
Targeting Groups: (Small Molecules, Peptides and Antibodies/Proteins)
| Small Molecules | Peptides |
|---|---|
|
|
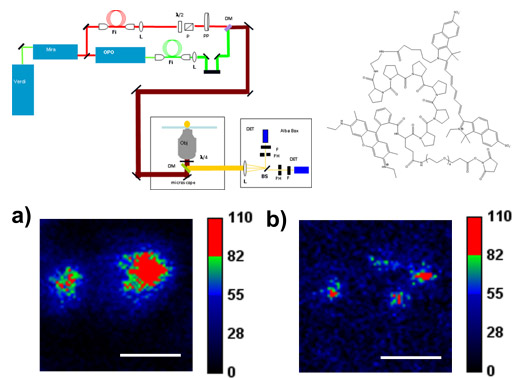
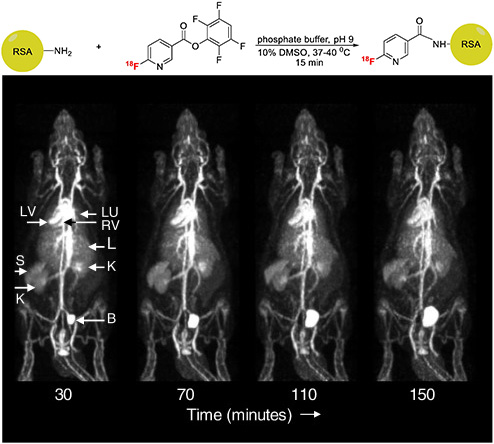
| Automatedsynthesisof[18F](2S,4R)-4-fluoroglutamine on aGETRACERlabTM FX-NPromodule | STAQ: A route toward low power, multicolor nanoscopy |
MRI Imaging (Hyperpolarized*, Dendrimer, Iron Oxide Nanoparticles)
| Dendrimers | Iron Oxide Nanoparticles |
|---|---|
|
|
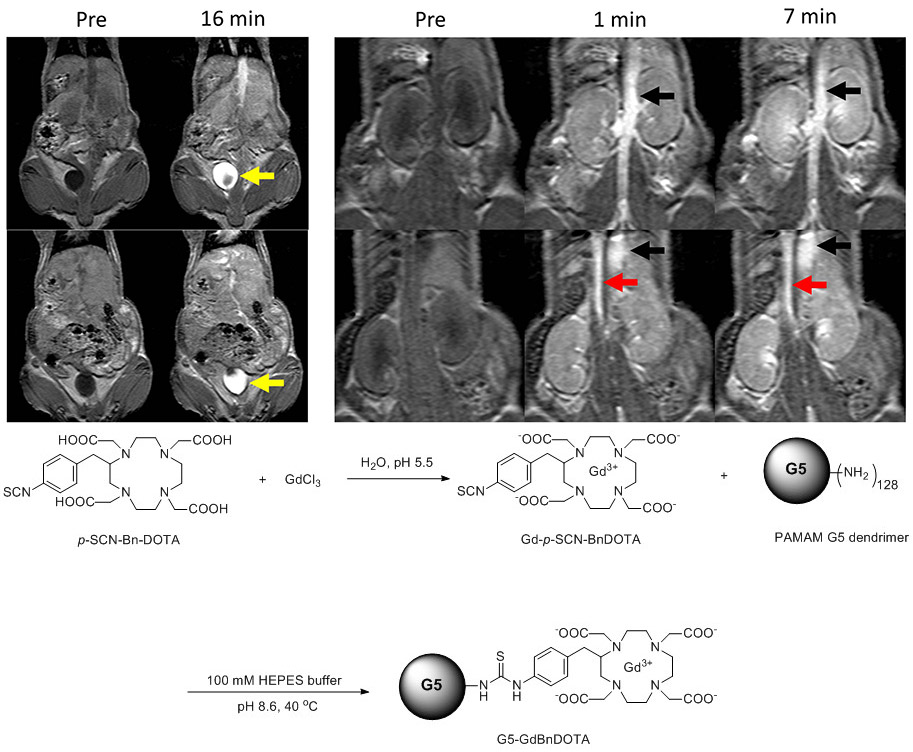
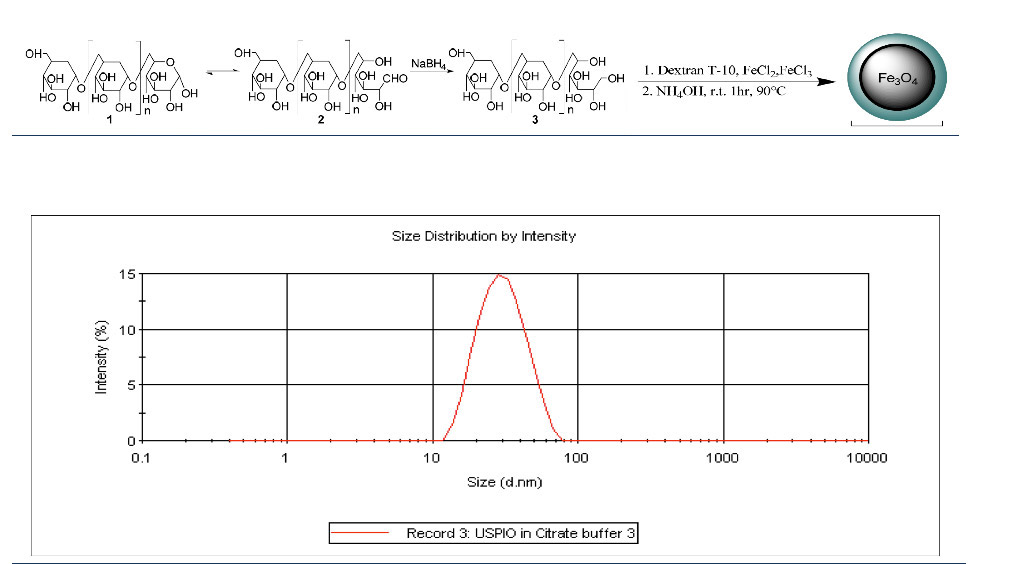
| Preparation and long-term biodistribution studies of a PAMAM dendrimer G5-Gd-BnDOTA | Synthesis of Ultrasmall Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for fMRI |
PET & SPECT Imaging (18F, 125I, and 89Zr)
New Offerings
- PROTACS (Proteolysis-targeting chimeras)
- Metabolomic feature identification
- Fragment based lead optimization by NMR
- Targeted nanoparticles (Fe, Au, C)
- Peptide optimization and multimerization
- Small Molecule Synthesis
I. PROTACS - Proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACS) are a small molecule based approach to knocking out a specific protein. Similar to siRNA or CRISPR-Cas9, a PROTAC can degrade a target protein via the native proteasomal machinery, without genetic modification to the cell. CSC works with PIs to collaboratively design and synthesize PROTACS to degrade specific proteins of interest.
II. Metabolomic feature identification - The presence and amount of a specific metabolite in cells, biofluids, tissues, or organisms can be directly reflective of biochemical processes occurring in a biological system in response to its environment. In a typical untargeted metabolomics experiment, hundreds to thousands of features are identified by HPLC or GC retention time – MS m/z pairs (features). The CSC can identify putative features and confirm by preparing noncommercially available authentic standards (and labeled analogs). We don’t perform the metabolism studies.
III. Fragment based lead optimization by NMR- NMR techniques are employed to generate high affinity ligands by identifying, optimizing and linking two small organic molecules to bind at proximal subsites of the protein. “SAR by NMR” is an approach where structure-activity relationships (SAR) are obtained by NMR.
IV. Targeted nanoparticles (Fe, Au, C) - Targeted nanoparticles have multiple uses in fluorescent and MRI imaging. The ability to manipulate the tissue uptake and biodistribution of these moieties relies on a highly tailorable and fully accessible surface. The introduction of various functional groups can be used to solubilize, reduce aggregation, and attach drugs or biomolecules to the nanoparticle. The CSC has prepared targeted Fe and Au nanoparticles as well as fluorescent nanodiamonds.
V. Peptide optimization and multimerization - We have expertise in peptide design, and use solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) to investigate SAR of sequences of interest to increase potency, metabolic stability, and water solubility. We can synthesize multimers to increase potency based on avidity. In addition, we also offer solution phase synthesis of complex peptides where SPPS is not effective. We have experience in derivatization of peptides with reporter moieties, e.g. dyes, macrocycles for chelation and precursors for radiolabeling.
VI. Small Molecule Synthesis - Medicinal chemistry leads and potential drugs from the literature are widely used as chemical tools for studying biological functions. We routinely synthesize compounds from the literature, perform hit to lead optimization for screening efforts, and derivatize heterocycles with fluorescent or Raman tags or chelates.
Other Offerings
- Fluorescent probes
- Hyperpolarized probes for MRI
- Lanthanide chelates for MRI
- 89Zr and 18F PET probes
- Liposomes, protein purification, and antibody digestion
I. Fluorescent probes - Fluorescence remains the premier approach to monitoring occurrences on a cellular level, with approaches that grow ever more sophisticated. CSC synthesizes custom fluorescent and light-activated probes, including fluorophore-labeled peptides, fluorescent or photoactivated drugs, fluorescent versions of native biological small molecules, and other literature-reported fluorescent tools, for biological research.
II. Hyperpolarized probes for MRI - Hyperpolarized contrast agents can be used to track metabolism and monitor characteristics of the tissue microenvironment by MRI. NMR hyperpolarization techniques enable a wide range of functional MR imaging from the lungs to metabolic imaging of cancer, and are ideal for the imaging of minor changes in small molecules such as fumarate, choline, and glutamine. The CSC routinely prepares isotopically labeled metabolites for the use in these studies.
III. Lanthanide chelates for MRI - The unique paramagnetic properties of the lanthanide ions render them useful as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents and paramagnetic relaxation enhancement or pseudo-contact shift (PCS) tags in structural NMR applications. CSC has experience in the generation of lanthanide(III)-chelates and adducts.
IV. 89Zr and 18F PET probes - Positron emission tomography (PET) provides information not only on biochemical, physiological and pharmacological processes but also offers the opportunity to study pharmacokinetics, metabolism, and mechanisms of action of novel and established drugs. We work with fluorine-18 and zirconium-89 PET isotopes to develop new probes or produce already existing probes. More than 40 different probes have been provided to the NIH investigators with an average of 150 production batches/year.
V. Liposomes, protein purification, and antibody digestion - Large molecule expertise at IPDC includes conjugation of proteins and peptides, antibody digestion, and protein purification. Antibodies and antibody fragments can be modified with chelating groups and fluorescent dyes. Encapsulation of drugs in liposomes can improve delivery and solubility. Liposome formulations can be prepared and extruded on a small scale.
Meet the Team

Rolf Swenson, Ph.D.
Rolf Swenson received his Ph.D. in synthetic organic chemistry at Cornell University working with Professor John McMurry. After post-doctoral study with Professor Wolfgang Oppolzer at the University of Geneva Switzerland, and Professor Hector DeLuca at the University of Wisconsin Madison, he joined Abbott Laboratories as a medicinal chemist. He moved to the combinatorial chemistry group and was a group leader working on rapid parallel synthesis. He then moved to Orchid BioSciences as a Director of Chemistry in charge of combinatorial chemistry in microfluidic devices, and while there led a project team that automated SNP genotyping to perform 1,000,000 genotypes/day. He left Orchid to become the International Area Head for Discovery Chemistry at Bracco Research USA. He led a team that prepared diagnostic imaging agents for PET/SPECT, Contrast enhanced ultrasound, MRI and optical applications. When the Princeton research facility was closed, Dr. Swenson started Arroyo BioSciences, LLC, which focused on discovering new drugs for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and other fibrotic disease. Since the beginning of 2014, Dr. Swenson has been the Director of the Imaging Probe Development Center, where he has managed a group of chemists who prepare chemical tools including diverse diagnostic probes for the intramural community. He is an inventor on 65 US patents and an author on 52 scientific papers. He has contributed to one approved drug, five other compounds advanced to clinical trials, 87 papers and 70 US patents.
Contact the lab

Falguni Bhattacharyya, Ph.D.

Burchelle Blackman, Ph.D.

Chandrasekhar Mushti, Ph.D.
Jess Benjamini-Ettedgui

Natarajan Raju, Ph.D.

Zhen Shi, Ph.D.

Olga Vasalatiy, Ph.D.

Haitao Wu, Ph.D.